DIY Search Engine Optimisation
Search engine optimisation or SEO refers to the actions you take to increase your page rank on Google and other search engines. We've put together a collection of DIY SEO tips to help you with this important website task:
- Understanding SEO Jargon
- Keyword research tools & tips
- Where & how to use keywords within your website
- Why unique content is good for SEO
- Outgoing, incoming and internal links
- Domain name considerations
- Adding new content
- Site maps and Webmaster Tools
- CMS Considerations
- Other things you might like to consider
Understanding SEO Jargon
- Keywords and keyword phrases - these are the words and phrases someone enters into a search engine to find information online.
- Keyword research - identifying the words and phrases someone uses to find information using a search engine. Learn how to complete your own keyword research here.
- Google - the world's most popular search engine. Others include Bing, Baidu, DuckDuckGo and Yahoo.
- Meta tags - a technical term for hidden text on a website page which tells search engines about that specific page. Learn more about meta tags and how to optimise them on your website here.
- Meta title - this is the text that is partially visible on your browser window title bar
- Meta keywords - refers to the focus keywords of a specific page, which should also be used somewhere within the page.
- Meta description - a human readable description of your web page that may or may not be used in search results. Learn how to write a meta description here.
- Page heading - (or H1 heading) - the page heading is normally the first human readable and largest heading on your page. It can be found at the top of your content, and beneath any graphical banners.
- First paragraph - refers to the first human readable paragraph of text on your page. It is typically one to three sentences which follow your H1 page heading.
- Sub headings - these are headings below the page heading which help to make the content easier to read. You can also allocate each sub heading a level of importance from H2 to H5, helping search engines identify important information.
- Link text - also known as hyperlinked text, this is the text that is underlined, that you might click to go to the destination link. The destination could be another page in your website or to another website.
- ALT Text - Hidden text behind an image that describes the image for an image search or for the blind.
- URL - This is similar to a web address, except the URL is longer, and every page on your website has a unique URL so that search engines can point to a specific page. For example, the web address is www.mysite.co.nz and a URL for that address could be www.mysite.co.nz/about-us
Keyword Research Tools & Tips
An important SEO tool, keyword research involves identifying the words and phrases people use to find products, services or information using a search engine. From here you can create content for your website that your target audience is looking for, increase website conversion rates, and rank higher in search results. Our article What is Keyword Research explores this area in greater detail.
There are both free and paid tools available to help you find these keywords and phrases, including:
- Google Trends
- Ubersuggest
- Answer the Public
- Google Search Console
- Keyword Revealer
- SEMrush
- Moz Keyword Explorer
- Wordtracker
- Keyword Tool
- KWFinder
- Keyword Planner
Another traditional tool you could use for keyword research is the Google search engine itself. In the past this was seen as the go-to tool, but one which is rarely used in isolation today.
Our tips for when researching keywords and phrases include:
- Think about the product or service keywords that someone would enter in a search engine trying to find a business "like yours".
- Consider the geographical word that someone might likely search for. Trades people would be searched by a suburb or town name. Where as a specialty food store, or small appliance store, might be searched by city, state or country name.
- Consider all the synonyms and sub classifications. E.g., if you sell shoes, you need to specifically state that you also sell "footwear, sneakers, high heels, slippers and flip flops". You need to consider all permutations of your keywords and the sub classifications thereof.
- Consider using non plurals even when plurals might seem your first choice, but use both. All words with different suffixes do return different results.
- Consider focusing on problems and symptoms. If your product or service is a solution to a problem, then it might be the ailment someone searches for, not the cure. This applies to other industry problems, not just health.
- Review the keywords in your web statistics. It tells you want words are working for you, but not the ones that are not. However, it might give you some hints for better words.
- Don't worry too much about your company name. If someone is searching for your business name, then they will likely find you. Just to be sure, you want your business name appearing more times on your web pages that any other website. So your business name should be listed on the bottom of every page in the copyright area.
- If one of your keywords is too generic or too competitive, don't worry. Try focusing on a niche market. In a small country you might provide a broad range of services, but internationally, you should target a niche. Better to be at the top of your niche, than half way down any other list.
- Whatever keywords you do select, make sure you actually use them in your website content. Search engines might look smart, but they are not. They cannot see your pictures nor make word associations. So if you have pictures of shoes on your website, it doesn't hurt to state categorically that "we sell shoes".
Where & How to Use Keywords Within Your Website
Next you'll need to add the keywords and corresponding information within your website. This needs to be done at both the front (page content) and back (meta tags) areas of your site, which is called on-page SEO. While you are doing this, remember that each page is an opportunity to be found and displayed by Google in its search results. Ensure each page has a unique keyword and content, as you don't want to be competing with yourself in Google!
When adding keywords to individual pages at the front end of your website, remember:
- use only one keyword or keyword phrase per page, including it in the page headings and paragraphs. Aim for the keyword phrase to feature in around 2-3% of the text, as using it too many times will have a negative effect on your search engine rankings.
- each page title needs to include the keyword phrase, which is known as the H1 heading (most important heading).
- include the keyword in at least one subheading on a page, known as the H2 heading (2nd most important heading) up to H5.
- the content at and towards the top of a page is the most important. Use the keyword phrase within the first few sentences and paragraph. Using synonyms for your keyword is beneficial and helps avoid keyword stuffing.
- keyword stuffing (adding the keyword phrase in large quantities on a page) should be avoided at all cost as Google can penalise your website
- when uploading an image via the wizard, consider using the "alt text" to insert keywords for your images. Other images will be automatically coded to the product title or gallery page title. You can also right click on an existing image, edit properties, and update the title/description there also
- include your company name on the footer of your website design - on all pages. This is normally taken care of for you by a copyright message, which serves this dual purpose. Consider including your suburb, town, city and country in the copyright line, as this will partially associate all your page content with those regions, increasing the likelihood your page will be found during a geographical search. You may also like to consider replacing the word "we" or "us" from time to time with your company name
Adding keywords to the backend of your website is done under the SEO section of the CMS, mainly the meta tag areas. In here you should add your keyword phrase in your meta tags if possible, including the meta title, meta description and filename.
- button title - the text you want shown on your menu for a specific web page. It should be short (one or two words) and say what the page is about
- page heading - shown on an actual page, this heading will automatically be given h1 status, which means that search engines will know that this heading is the most important one on your page. Your page title should accurately describe what the page is about and contain your page's keywords
- meta title - seen in a page browser tab, aim to use around 60 characters (spaces, letters, symbols) in your meta title (more is fine, but search engines tend to only display up to 60 characters). It should contain the page's keyword and describe what the page is about, like a shorter version of your page heading
- description - also known as a meta description, this short blurb which is shown by search engines on their search results pages. The amount of text shown can vary between search engines, with Google generally showing around 150 characters per result (letters, spaces, symbols or numbers). Ensure it is 100% original, contains your keyword, gives a short teaser of what is contained in the article and includes a call to action
- keywords - while you can add multiple keywords in this box, remember that each page on your site should focus on only one single keyword or keyword phrase
- filename - the end piece of your URL which comes after the /. Aim to keep it short yet descriptive, including your keywords where you can. It is best practice to use hyphens between words in your filename
Why Unique Content is Good for SEO
Search engines use complex algorithms to identify which sites have the best quality unique content so they can present users with the most relevant results for their search. Unique content is the content that is present on your website only, helping to distinguish it from other websites. As well as providing valuable information for website visitors, original website content is vital for SEO because it helps to:
- get more organic traffic to a website from search engines
- help raise your domain authority or DA, which is a credibility ranking given to a website
- quality content gives your website authority
- achieve more backlinks, as others share your content as they view it of benefit to their audience
- rank higher in search engine results pages or SERPs
- improves user experiences
Website visitors will not always come to your home page first. Everyone has a different problem they want to solve, or a specific product they want. Consider searching for "Hamilton Accommodation" and seeing the results for "AA travel" or "Jasons" websites. If you clicked on those websites you would not expect to go to their home page, you would expect to go to the page most applicable to your search phrase: "Hamilton Accommodation"
Dedicate one page on your website per key phrase. A significant proportion of all Google searches will cause a a customer to come to a "landing page", not your home page. So optimise certain pages of your website to be landing pages for each key phrase. Think of your website as a fishing line with lots of different hooks. You never know what fish is lurking, and you need to have the right hook for the right fish.
Incoming Links
Incoming links are links from other websites to your website, and are used to share information with the originating website's audience. Search engines use incoming links as one of their many SEO ranking factors. Just as your website is ranked according to unique content and other factors, so are the sites that the incoming links are from. The higher the quality website, the more importance a link is given. In the diagram below, Retailer D has the most beneficial links and theoretically the highest ranking website, followed by C, B and then A.
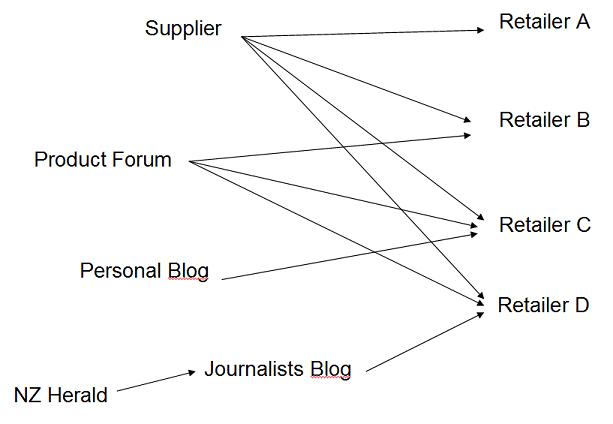
Incoming, Outgoing and Internal Links
- Once you are found by Google, the next most important thing you can do to increase your search rank is incoming links. An incoming link is a link from another website to yours. This is like the other website is referring business to you, or endorsing you, or advertising you. In plain English this is a good thing. The more the better. Incoming links increase your traffic. To get an incoming link, you need to ask (and possibly pay) the other website to set this up for you.
- Outgoing links are not good. These are links that take people from your website to another website. Not only has that ended the chance for you to complete a sale, but you are also negating any value of any incoming links. You should want more incoming links than outgoing links. If you do link out, make sure that the link opens a new page, so the user doesn't leave your page.
- Internal Links - These are links from within the content of one of your pages linking to another page on your website. These types of links help identify and control the relevance of more important pages in your website.
Anchor or Link Text
- To maximise the benefit of your incoming links, you should also consider what the link text says. Where possible provide the other website with the link text you want them to use. Avoid link text that is merely your web address, company name or "click here". Make it a clear key phrase like "Cheap shoes at Johns Shoe store". Using key phrases in link text will improve your ranking for those words a lot.
Where to get incoming links from?
- Business Directories, Paid and Free. Different industries have all sorts of directories relevant only to them. One of the hottest online NZ based business directory is Business Networking NZ. It offers a free link to your site and a supportive Facebook networking group to join and chat with other business owners too.
- Suppliers or customers
- Members of your organisation, or industry associations you belong to
- Wikipedia articles
- Government directories, there are heaps of government owned directors including those related to major sporting events like the Rugby world cup, or the ministry for economic development.
- Forums, Blogs and Social Networking sites
- Submit your site to as many search engines as possible. It takes time, but it's worth it.
- Create social networking profiles, with links back.
- Join Marketplaces, eg OurMarket
- Site Maps - This is a good way to identify all the pages of your website so that Google can at least easily find all your web pages. Your website world sitemap is located at www.yourdomain.name/sitemap.xml
Local SEO - Local Retail / Services / Trades
Because of this, if your business serves your local area, it is vital that you include the names of the town, city and region you operate in throughout your website such as in headings, paragraphs and footer.
Domain Name Considerations
- Older domain names and websites that have existed for a long time, without any outages, typically rank higher than newer websites, even if the content has not been updated for ages.
- Domains that are registered several years in advance, set them selves apart from domain squatters that cannot afford to renew 1000's of domains years in advance. It is a small cost to a business owner to renew only 1 domain several years in advance, and Google can easily determine this small piece of information.
- Using a domain name with keywords in it is obviously better than one that doesn't, but don't change your old and successful domain name just for the sake of it. you will lose all that history and rank you built up over the years.
- You only need one domain name for Google. It will mostly ignore your other domains. Some argue you should have redirections from all your other domains
- Having a .nz domain suffix can rank more highly in Google.co.nz.
- With our CMS, you can register additional domain names and have them "mirror hosted" in other countries. We will mirror your website free of charge on those other domain names. So you can get the same geographical search benefits in those other countries local instance of Google.
- There are many different domain suffixes available, with .com .co.nz and .nz being a few examples. Generally you should have the suffix which is appropriate to the countries you operate in or related to your industry
Adding New Content to a Website is Beneficial
As well as unique content, your website will also benefit by you adding new content regularly because:
- new content encourages repeat indexing of your website by search engines
- the more content your site has, the more opportunities it has to be show in search engine results
- fresh content helps to increase your domain authority
- visitors are encouraged to revisit your site to check out what is new and remain engaged with your brand
Site maps and Web Master Tools
- Google Web Master Tools and Bing Web Master Tools will help you get your new website found more quickly
- It will help you fix any errors that occur with your website search results.
- It will improve your ranking. Refer to the link for more info.
- You can download a site map in the SEO area of our CMS
CMS Considerations
- Take care on your choice of web designer or content management system. Some CMS do not make websites which are search engine friendly, such as where the URL's to each page are different each time a robot visits due to a session ID, or the URL's are long and unfriendly to read. Other downfalls of some CMS are that the template design code obscures the content, or uses important tags like H1 for logo or company name placement, rather than immediately preceding the first paragraph.
- A good CMS to use is , Website World Content Management System which generates web pages suitable for indexing by search engines and does not fail any of the tests above. Web Widgets also provides an easy way for you to update your keywords and meta tags without technical expertise, and provides helpful tips along the way.
Web Statistics
- It's important to monitor how your website is working for you.
- You can view your web statistics free of charge by logging into the CMS, and you can also have them emailed to you on a regular basis.
- The statistics package we have integrated with our CMS is AWstats. It provides good easy to read results, and is known as a server side stats package. You may also like to consider Google Analytics which can give you more information about the size screens that customers use, as they are client side stats collectors.
- Where can I insert Google Analytics?
- There is an area to do this in the SEO or custom design settings or under the domain name statistics and SEO area.
- You can also insert specific Google Analytics tracking code for monitoring advert "conversions" to a enquiry form thank you page or shopping checkout page. Use the insert Video function in the tool bar or go to HTML mode and scroll to the very bottom and paste it there.
Pay Per Click
- Adwords is an option you might like to consider for immediate results.
- Make a different advert for each key phrase (or set of similar phrases) you are targeting. The advert will be more effective if it is highly relevant to the searcher keywords. The searcher knows what they are looking for, your advert needs to speak to the searcher, it speaks loudest if your advert heading includes their keywords.
- With pay per click, budget is an important factor, so only make adverts for key phrases of 3 words or more. Your advert might be shown to less people, but at least you know it will only be clicked on by the people who really want your services. If you spend less on the wrong people, you can spend more on the right people or enter new markets.
- Target only 1 market at a time, until you learn the ropes. If you enter a new market (country / language), make sure your website is ready to support them.
- Make sure your advert link goes to a page highly relevant to their needs. This will quite likely not be the home page. Put yourself in your customers shoes, they don't know you, they searched for some words, found your advert, now what? Make sure the next sentence they read on your website flows obviously from the wording of your advert. So quite likely you will have a different landing page for each advert.
- Learn more about Adwords and Cost Per Click Advertising
Other things you might like to consider
- Avoid the excessive use of Flash on your website. Most graphic designers who use a lot of Flash forget to do the most basic of search engine optimisation - including page titles, keywords, and alternative (non flash) representations of the website. Flash sites look good, but you can hardly ever find them in search engines.
- Goggle's new search relevance buttons, users are making their own decisions about the relevance of pages
- Google tool bar page rank, this sends information to google as to what pages you look at, even if those pages are book marked or entered directly to the address bar from a business card. This helps google make decisions about which websites are more relevant even if not searched for.
- SEO best practices are always changing, so keep updated. Google Search Central is a good place to do this.
- Get a nicely formatted report of how your website SEO is going, and includes some more tips and tricks peculiar to your needs at Website Grader or Moz
Don't wait, do it now! When it comes to SEO, you are in it for the long haul. It takes time to get new websites and new content shown by Google, and you can expect your rankings to go up and down a lot with algorithm updates.

